Noticias
Atom Silvermont, Intel pone entre las cuerdas a ARM

Intel está preparando una nueva arquitectura de CPU bajo la familia Atom que promete ser hasta tres veces más rápida que la generación anterior y nada menos que 5 veces más eficientes energéticamente, es decir, tienen un consumo de una quinta parte frente a la generación actual de Atom.
Esta nueva arquitectura se conoce como Silvermont y está enfocada en smartphones, tablets, PCs y servidores este año. Será la generación posterior a los inminentes de Intel Bay Trail que verán la luz este verano con soporte tanto para Android como para sistemas Microsoft.
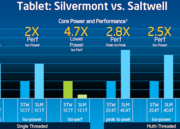
Los nuevos chips para tablets serán más de dos veces más rápida en rendimiento monohilo frente a la arquitectura actual –Saltwell-. Esta información ha sido confirmada por parte de Intel durante el briefing de este lunes. Usando la misma métrica ha comentado que este chip tiene un consumo 4,7 veces menor que sus predecesores.
La arquitectura Silvermont puede escalar hasta 8 núcleos y es, sin duda, el mayor rediseño de la arquitectura Atom desde el primer chip de la familia que vio la luz en 2008 en la generación original de netbooks.
Intel quiere entrar en el segmento tablet y de smartphones que está repleto de soluciones basadas en ARM. De hecho Intel quiere romper el mito del «imbatible» rendimiento por vatio de la arquitectura ARM.
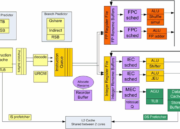
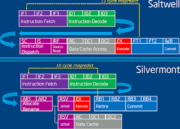
Entre otras mejoras Silvermont integra Out-of-order execution que permite el proceso de instrucciones de manera más eficiente. Además tambiént se tiene más ancho de banda interna que permite interconectar de manera más rápida los núcleos CPU con la GPU. Silvermont también incluye las últimas tecnologías de virtualización y seguridad.
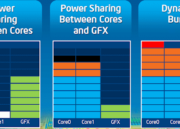
Los núcleos también son flexibles en rendimiento y consumo de energía ya que los núcleos pueden aumentar en frecuencia o incluso ser apagados para ahorrar energía, lo que se convierte en una mejor solución que la tecnología Big.Little de ARM.
La arquitectura Silvermont permite que la energía entre los núcleos de CPU y GPU gracias a algoritmos que monitorizan el consumo energético y permite bajar el consumo según el tipo de dispositivo. Además promete que se puede resumir desde reposo mucho más rápido.
Los Atom Silvermont estarán fabricados en proceso de 22nm con transistores 3D, siendo más eficientes energéticamente y también más pequeños que con Clover Trail, fabricados en 32nm. Intel está trabajando en el proceso de fabricación de 14nm que dará lugar a la siguiente generación Atom Airmont.
[expand]
Intel Corporation today took the wraps off its brand new, low-power, high-performance microarchitecture named Silvermont. The technology is aimed squarely at low-power requirements in market segments from smartphones to the data center. Silvermont will be the foundation for a range of innovative products beginning to come to market later this year, and will also be manufactured using the company’s leading-edge, 22nm Tri-Gate SoC manufacturing process, which brings significant performance increases and improved energy efficiency.
«Silvermont is a leap forward and an entirely new technology foundation for the future that will address a broad range of products and market segments,» said Dadi Perlmutter, Intel executive vice president and chief product officer. «Early sampling of our 22nm SoCs, including «Bay Trail» and «Avoton» is already garnering positive feedback from our customers. Going forward, we will accelerate future generations of this low-power microarchitecture on a yearly cadence.»
The Silvermont microarchitecture delivers industry-leading performance-per-watt efficiency. The highly balanced design brings increased support for a wider dynamic range and seamlessly scales up and down in performance and power efficiency. On a variety of standard metrics, Silvermont also enables ~3x peak performance or the same performance at ~5x lower power over the current-generation Intel Atom processor core.Silvermont: Next-Generation Microarchitecture
Intel’s Silvermont microarchitecture was designed and co-optimized with Intel’s 22nm SoC process using revolutionary 3-D Tri-gate transistors. By taking advantage of this industry-leading technology, Intel is able to provide a significant performance increase and improved energy efficiency.Additional highlights of the Silvermont microarchitecture include:
- A new out-of-order execution engine enables best-in-class, single-threaded performance.
- A new multi-core and system fabric architecture scalable up to eight cores and enabling greater performance for higher bandwidth, lower latency and more efficient out-of-order support for a more balanced and responsive system.
- New IA instructions and technologies bringing enhanced performance, virtualization and security management capabilities to support a wide range of products. These instructions build on Intel’s existing support for 64-bit and the breadth of the IA software installed base.
- Enhanced power management capabilities including a new intelligent burst technology, low- power C states and a wider dynamic range of operation taking advantage of
- Intel’s 3-D transistors. Intel Burst Technology 2.0 support for single- and multi-core offers great responsiveness scaled for power efficiency.
«Through our design and process technology co-optimization we exceeded our goals for Silvermont,» said Belli Kuttanna, Intel Fellow and chief architect. «By taking advantage of our strengths in microarchitecture development and leading-edge process technology, we delivered a technology package that enables significantly improved performance and power efficiency ? all while delivering higher frequencies. We’re proud of this accomplishment and believe that Silvermont will offer a strong and flexible foundation for a range of new, low-power Intel SoCs.»
Architecting Across a Spectrum of Computing
Silvermont will serve as the foundation for a breadth of 22nm products expected in market later this year. The performance-per-watt improvements with the new microarchitecture will enable a significant difference in performance and responsiveness for the compute devices built around these products.Intel’s quad-core «Bay Trail» SoC is scheduled for holiday 2013 tablets and will more than double the compute performance capability of Intel’s current-generation tablet offering1. Due to the flexibility of Silvermont, variants of the «Bay Trail» platform will also be used in market segments including entry laptop and desktop computers in innovative form factors.
Intel’s «Merrifield» is scheduled to ship to customers by the end of this year. It will enable increased performance and battery life over current-generation products1 and brings support for context aware and personal services, ultra-fast connections for Web streaming, and increased data, device and privacy protection.
Intel’s «Avoton» will enable industry-leading energy efficiency and performance-per-watt for microservers2, storage and scale out workloads in the data center. «Avoton» is Intel’s second-generation Intel Atom processor SoC to provide full server product capability that customers require including 64-bit, integrated fabric, error code correction, Intel virtualization technologies and software compatibility. «Rangeley» is aimed at the network and communication infrastructure, specifically for entry-level to mid-range routers, switches and security appliances. Both products are scheduled for the second half of this year.
Concurrently, Intel is delivering industry-leading advancements on its next-generation, 22nm Haswell microarchitecture for Intel Core processors to enable full-PC performance at lower power levels for innovative «2-in-1» form factors, and other mobile devices available later this year. Intel also plans to refresh its line of Intel Xeon processor families across the data center on 22nm technology, delivering better performance-per-watt and other features.
«By taking advantage of both the Silvermont and Haswell microarchitectures, Intel is well positioned to enable great products and experiences across the full spectrum of computing,» Perlmutter said.
[/expand]
-

 GuíasHace 6 días
GuíasHace 6 díasQué placa base elegir: Guía de compras para Intel y AMD
-

 GuíasHace 2 días
GuíasHace 2 díasGuía para diferenciar generaciones y gamas de tarjetas gráficas
-

 A FondoHace 6 días
A FondoHace 6 díasOfertas Flash del Black Friday 2024 de PcComponentes
-

 A FondoHace 4 días
A FondoHace 4 díasGeForce RTX 5050, especificaciones, rendimiento, equivalencias, fecha de lanzamiento y posible precio